The Exciting Science Of Hydroponics
In the 1800s, physiologists discovered that plants absorb much of their nourishment from mineral nutrients dissolved in water. The nutrients plants need are not normally present in water, but are absorbed when water comes in contact with soil and then carried into plants through their roots. This was an important discovery because it showed that soil itself is not an essential part of plant growth. Rather, it simply acts as temporary storage for the minerals that plants need.
![]()
Hydroponics works by artificially introducing these nutrients directly into a plant’s water supply. The most common method hydroponics gardeners use to do this is to purchase one of the many brands of concentrated nutrient solution on the market, mix it with water and regularly feed it to plants using whatever hydroponics technique is preferred. This completely eliminates the need for soil and helps ensure that each plant receives the optimal level of every essential mineral nutrient.
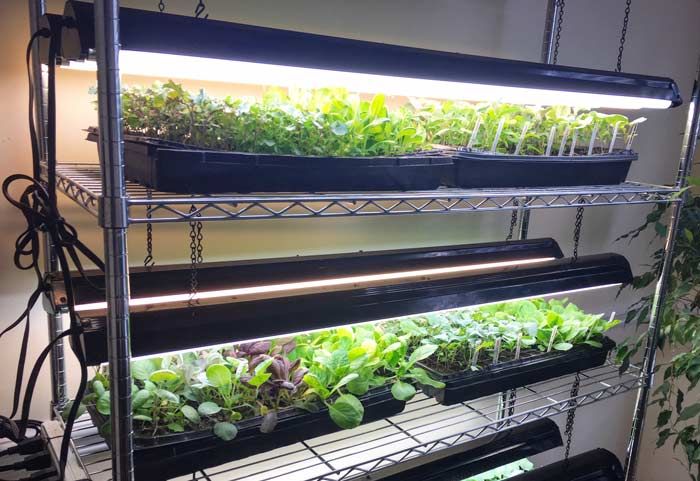
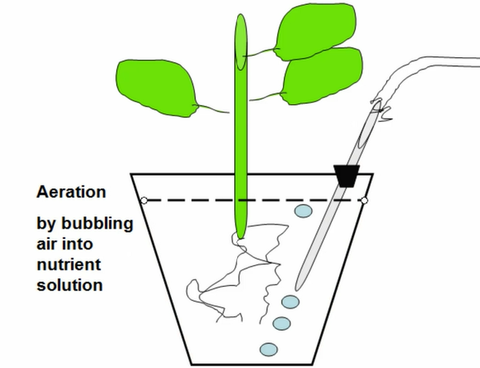
Plants can obtain the air they need in a number of ways. A good way to achieve aeration is to use a porous growing medium that traps air bubbles (such as vermiculite). Other options include constantly circulating the water in the system and even removing the plants’ roots from the water at regular intervals.
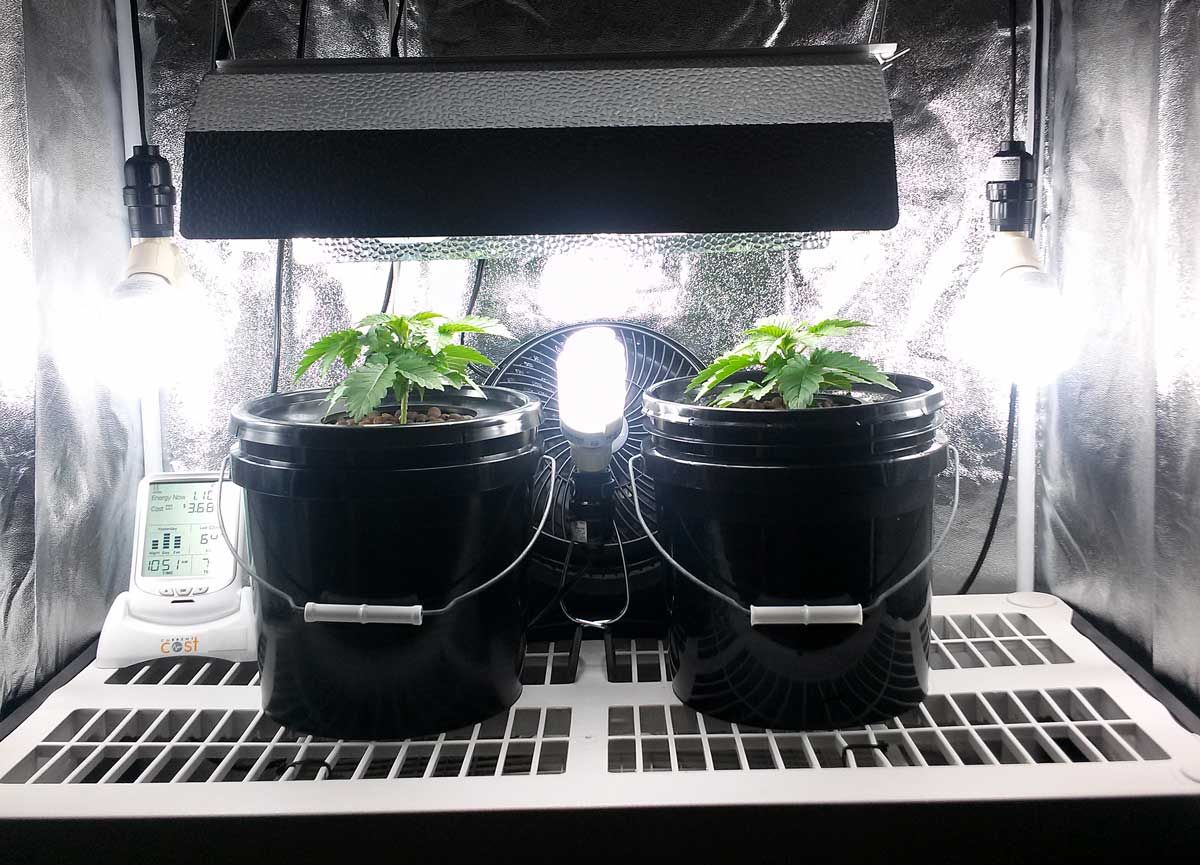
Artificial lights are often used in hydroponics systems – sometimes as the only light source and sometimes to augment natural light. The use of artificial lights makes it possible for plants to be grown indoors on a year-round basis.
Why Is Hydroponics Superior To Soil?
![]()
One of the main reasons hydroponics is so popular is that it produces healthier plants than soil-based gardening. This is because hydroponically-grown plants can focus their energy on processes that benefit the development of healthy leaves, flowers, and fruit. Plants grown in soil expend a great deal of energy on root growth. Their roots plunge down into the soil, searching for water and using up nutrients that otherwise could be put toward upper leaf development. In a hydroponics system, plants are always provided with easy access to water and nutrients, so they do not have to expend much energy on root growth. The result of this is that hydroponically-grown plants are able to develop at rates that are unheard of in soil gardening.
Any plant that grows normally in the soil can be grown hydroponically. However, some will perform better than others depending on the technique and equipment used.
Is Hydroponics New?
![]()
No, hydroponics is most certainly not new. Hydroponics has been around for centuries and has been used worldwide in many different countries for the production of food. A good example of its age is the use of hydroponics in the gardens of Babylon.
What Is Hydroponics Used For?
![]()
Many people often ask, what is hydroponics used for. Well, it’s quite simple as you can grow almost anything you desire. Vegetables, herbs, peppers, and flowers are all grown hydroponically and regularly supplied for the public to consume. Your weekly trip to the supermarket will provide you with many items that are grown hydroponically by large commercial companies and there are many restaurants and homeowners that nowadays use hydroponics to grow their own fresh produce.
Is Hydroponics A Reliable Method Of Cultivation?
![]()
Hydroponics is now becoming the most popular method of plant cultivation around the world, as it is the most reliable method for a regular source of fresh food to be produced, even NASA have used hydroponics as a means to raise crops in outer space, it really is out of this world.
What Methods Are There For Hydroponics?
![]()
Hydroponics is to supply a nutrient-rich solution to the inert growing media and roots to feed the plants and then re-circulate or run the excess solution to waste. There are various methods for hydroponics that are used and below are the main methods for hydroponics cultivation, which nowadays have also formed many hybrid hydroponic systems.
1. Aeroponics
![]()
Aeroponics Growing Systems are designed to support your plants in the top of the system, usually in mesh pots to allow the roots to be suspended below in the dark in a sealed container or tank and misted or sprayed constantly or regularly at timed intervals with a nutrient rich solution. Excess solution will drain from the roots and system and re-circulate back into the main storage tank for later use. Aeroponics is an extremely clean and efficient way to grow and requires very little growing media to support your plants, and with the large amounts of oxygen available to the roots, it is also one of the quickest methods of plant cultivation as well.
2. Deep Water Culture – DWC
![]()
Deep Water Culture is a very simple, yet very effective method for hydroponics. Plants are supported in the top of the system and the roots are suspended below in the dark sealed container or tank and submerged into a deep solution of water and nutrients that is constantly aerated and highly oxygenated by an air pump and stone. The flow of bubbles into the solution and around the roots allows the plants to flourish, and with a constant supply of water and nutrients, they grow very quickly. DWC is becoming a very popular method with growers, as it requires very little growing media and it is an easy way of growing with hydroponics.
3. Drip Systems
![]()
Hydroponic dripper systems are a favorite with many growers as they are very easy to use and they are also very reliable. Plants can be grown in pots, trays or slabs and irrigation feed lines will be placed into the top of the media to drip and deliver the nutrient solution directly where it is required to go. The solution will drain through the media to feed the roots and any excess nutrient solution can be re-circulated back into the main tank or it can be run to waste. A great example of a hydroponic top feed dripper system is a Drip Potz System, which is capable of re-circulating the nutrient solution back into the main tank, or it can be run to waste.
4. Flood & Drain – Ebb & Flow
![]()
Flood & drain systems do exactly what they say they do, which is to flood the system with a nutrient-rich solution to moisten the media and roots to feed the plants, and then they drain pulling air back into the media. Flood Potz Systems are a good example and these even combine DWC. As the Potz is flooded an air stone connected to the bottom of each mesh basket aerates the solution, media, and roots to provide the perfect environment for the plants to flourish, a failsafe method that provides the ultimate yields as well.
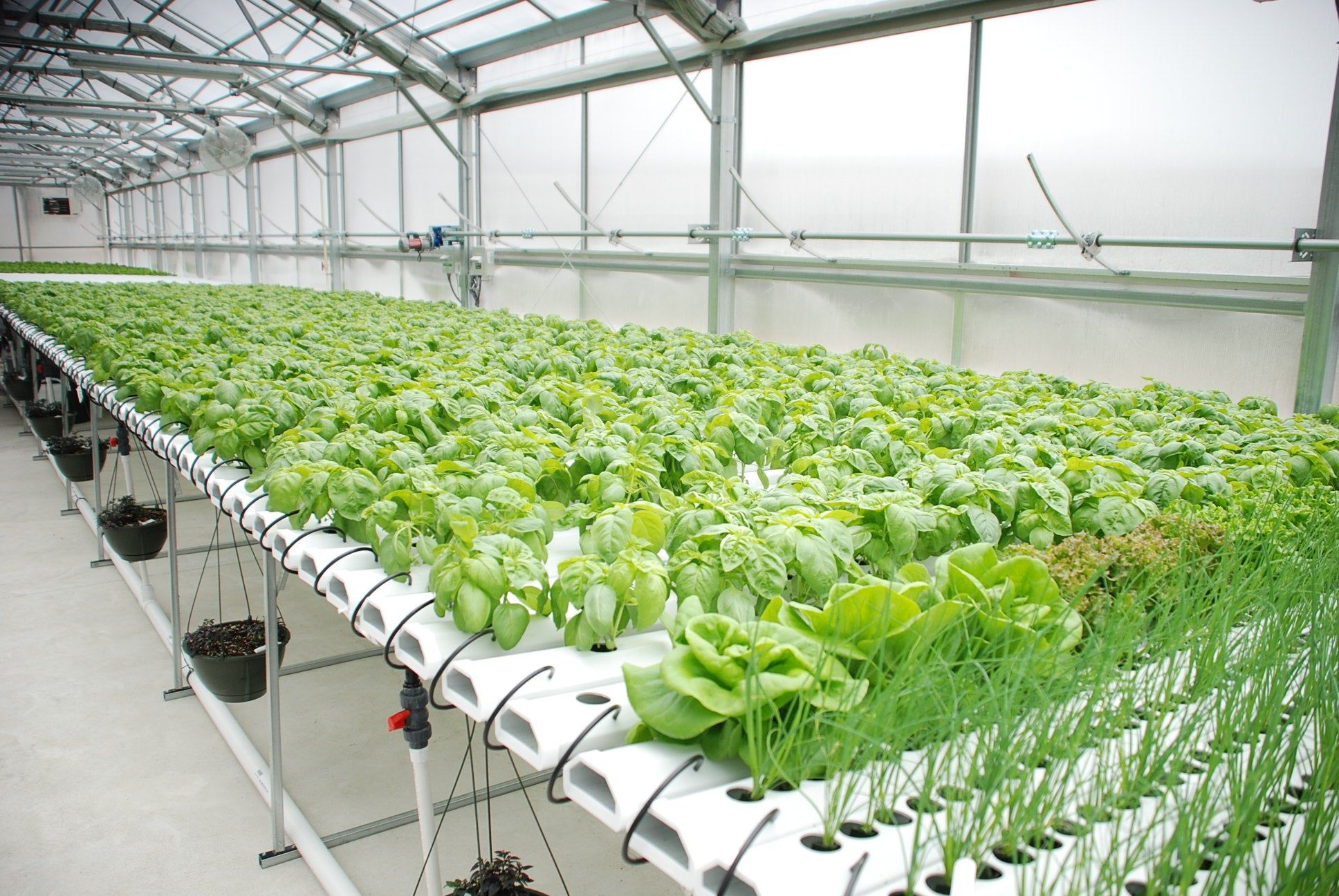
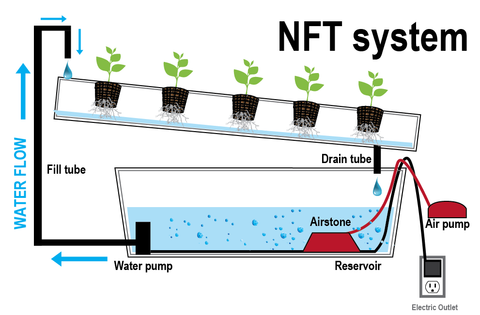
5. Nutrient Film Technique
![]()
NFT is probably the most popular method used for hydroponics. NFT Growing Systems use a sloped top tray to support and grow your plants on, and this tray is placed onto a tank or supported with a stand and a tank. A pump is placed into the tank to deliver your stored water and nutrients up into the high end of the top tray and with the slope, it will slowly fall across the tray and plant roots and back into the tank and re-circulate. Plants are usually grown in Rockwool blocks, which are sat onto the top tray when a good root system is established. A piece of correx (plastic sheet) is used and holes are cut out to position your plants on the top tray, the correx prevents the light penetrating your roots and affecting growth.
What Are Hydroponics Nutrients?
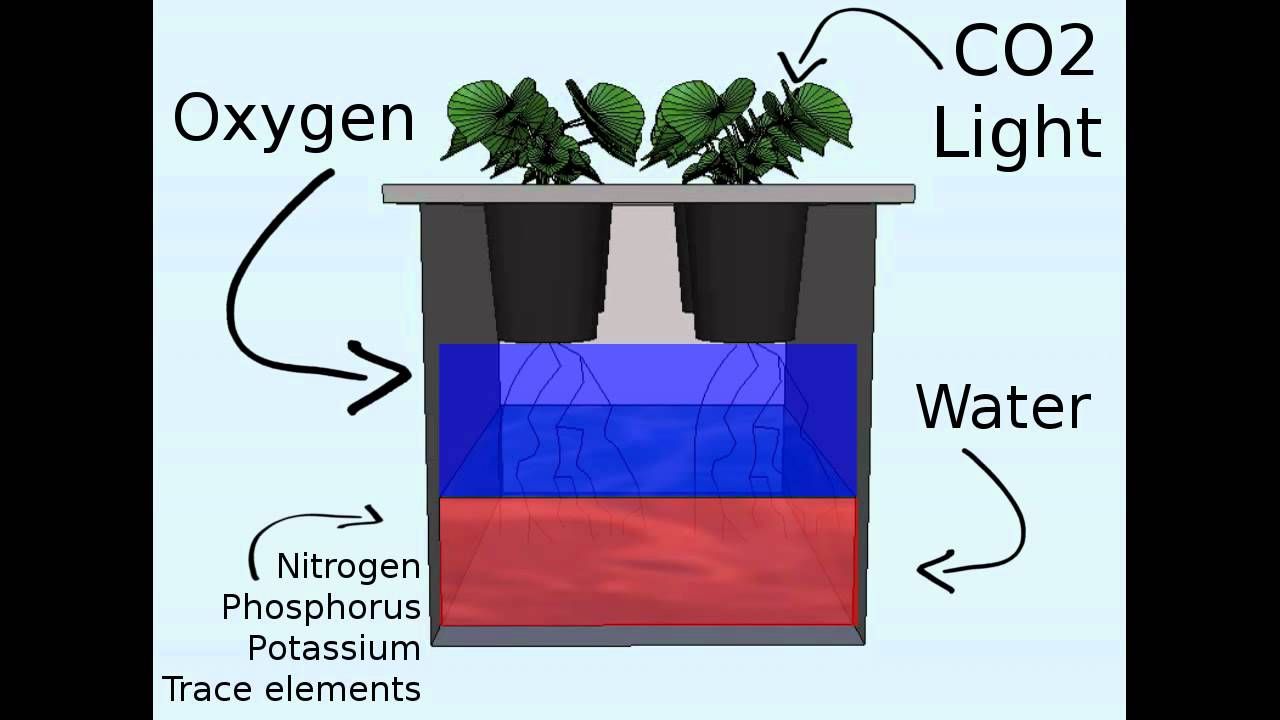
When plants grow outdoors with Mother Nature to help them along the way, they obtain natural minerals that lie beneath the ground through their roots to provide food for them to grow. Hydroponics growing media contains no nutritional content that can feed plants and also the water you supply, so the correct proportion of elements required for plants to grow and also produce flowers or fruits is provided into the water that is supplied to the roots to feed them.
![]()
Hydroponic Nutrients will contain macro-nutrients and micro-nutrients in a well-balanced form that can be easily absorbed through the root system and then broken down chemically within the plant. Macro-nutrients are the elements that plants require the most to grow, Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium (K) are absorbed through plant roots in very large amounts, with secondary macro-nutrients such as magnesium, calcium, and sulfur also required by plants in large amounts. Plant roots absorb micro-nutrients in very small amounts. Zinc, manganese, iron, boron, cobalt, and molybdenum are all micro-nutrients which will be available in a good quality hydroponic nutrient.
We stock only quality hydroponic nutrients from Canna, Plagron, Biobizz, Plant Magic and House & Garden, and if you choose to use one of them we have all of their Hydroponics Feed Schedules available to download. These should only be used as a guide, as different plant varieties will require different levels of food to be supplied.
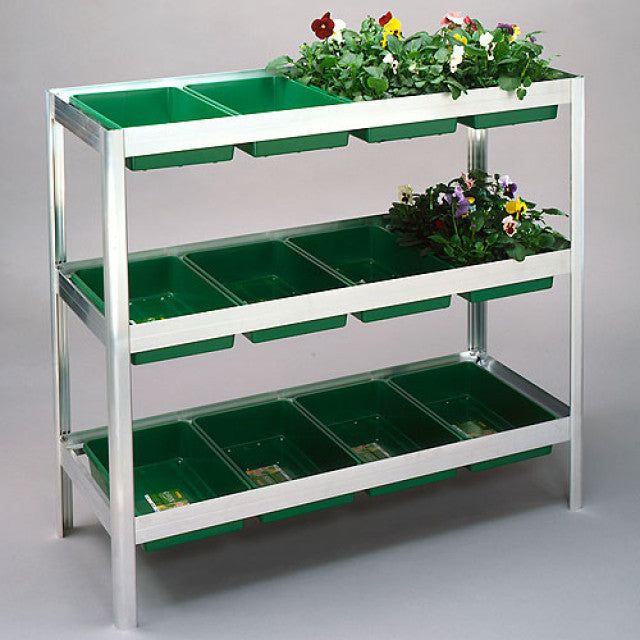
What Is Hydroponics Growing Media?
Hydroponics requires an inert growing media to be used, which is chemically inactive and contains no nutritional content as all the nutrients required by the plants to grow will be supplied in the water by you.
![]()
Hydroponics Growing Media is used mainly to support the plants that are being grown and allow the roots access to water, nutrients, and air at all times. This is one of the main reasons for hydroponics cultivation being so much quicker and better than soil grown plants. A soil grown plant will divide its energy into root growth and plant growth to ensure it uptakes any available nutrients, but a hydroponically grown plant is supplied with all the nutrients it requires directly to the roots and with higher amounts of oxygen also available, it allows the plant to concentrate more on plant growth.
The most common growing media used for hydroponics is expanded clay pebbles and Rockwool fibers as these both can hold oxygen, water, and nutrients very well and contribute to the plants’ ability to grow very fast. There are several other growing substrates that can be used for hydroponics, such as perlite, vermiculite, gravel, and foam, all of which can deliver some great results.
Irrigation feed times can vary with the different types of hydroponics growing media, and it will also depend on the size of your plants and the environment conditions in your hydroponics grow room.
What Are The Benefits With Hydroponics?
![]()
Hydroponics offers many more benefits when compared to normal methods of plant cultivation, especially when it is used indoors in a controlled environment.
1. Pests and Diseases
![]()
When growing indoors with hydroponics, the chances of pests and diseases occurring is very small, but if unfortunately, they do it can be far easier to treat and eliminate the problem. Hydroponics growing media is inert, containing no nutritional content so the chances of the growing media carrying any pests or diseases, is also very small if any. Usually, the main culprit who transports any pests or diseases into the grow room will, unfortunately, be you.
2. Maintain Weekly
![]()
Growing many plants in soil can be a tedious task with many hours spent on maintaining the garden and feeding the plants, but with hydroponics a garden can be set up and checked weekly for maintenance, as a large tank of nutrient solution can be left at the correct PH and EC levels and automatically fed to the plants daily in the hydroponic system.
3. Quicker Growth and Bigger Yields
![]()
As hydroponic systems provide the nutrient solution directly to the roots of the plants, the plants can put all their time and effort into vegetative growth up top. This provides much quicker growth from the plants and when growing fruit-bearing plants the yields that can be achieved cannot be matched with any other method of cultivation.
4. Grow All Year Round
![]()
When using hydroponics indoors under controlled conditions, you can grow any time of the year and produce a consistent, bountiful harvest all year round. The outdoor temperatures and light conditions throughout the year play a major role for commercial growers who depend on good weather and light, but growing indoors with hydroponics defies Mother Nature and allows you to continue growing all year round.
Is Hydroponics Better Than Soil?
![]()
Hydroponics is definitely better when compared to soil grown plants, the rate of growth and yield from fruit-bearing plants cannot compete from soil-grown plant to a plant grown hydroponically. Hydroponics supplies all water and nutrients directly to the roots of the plant and this means the plant does not have to develop a large root system to feed, but with soil the plant will divide its energy between growing upwards (plant vegetation) and also downwards (roots) to ensure a good supply of nutrients are available to the plant. To put it simply, a plant grown for ten weeks with hydroponics will be a lot bigger and stronger, yielding much more than a plant grown for ten weeks in soil, and if the plants are flushed correctly to remove all the nutrients before harvest, the taste from your fruits should be much the same.
What Do You Need For Hydroponics At Home?
![]()
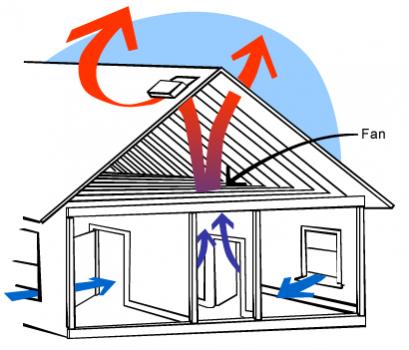
Now you have a clearer idea to what is hydroponics, you may well wonder what you will need for you to grow your own fresh produce at home and setting up hydroponics grow room at home couldn’t be simpler these days, with all the specialist equipment that is available. Hydroponics at home requires an enclosure for your grow room, which can be an empty cupboard or a grow tent and you will most certainly need a grow light. Apart from a hydroponic system, the other major items you will need are some fans, ducting and a carbon filter to control the environment inside your grow room.
“Plants are very much like humans, they require a night and day period and given a warm sunny climate with good food and plenty to drink, they will be very happy and flourish”








































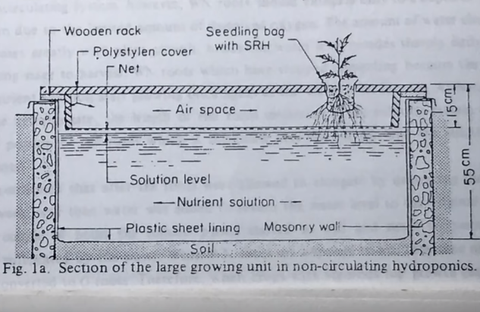
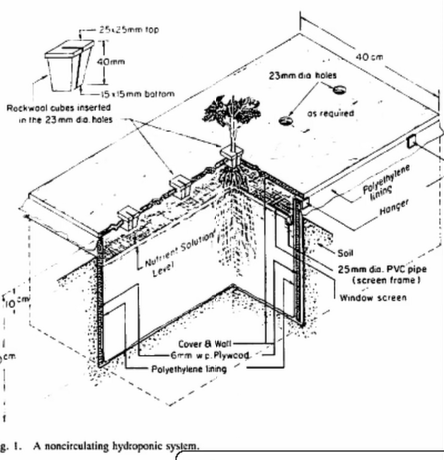
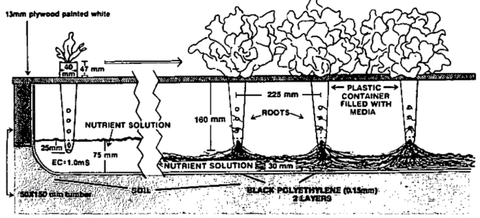
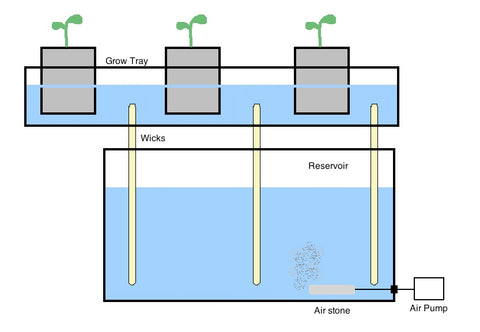 It is a passive system which means it has no moving parts. Nutrients move from the reservoir to plants roots by a wick or string. Plants can be housed in a variety of growing mediums some of which are coconut coir, perlite or vermiculite. Due to their simplicity, these systems are a great option for growing smaller plants. The drawback with this system is that they can be inefficient if not set up properly, plant growth will be hampered.
It is a passive system which means it has no moving parts. Nutrients move from the reservoir to plants roots by a wick or string. Plants can be housed in a variety of growing mediums some of which are coconut coir, perlite or vermiculite. Due to their simplicity, these systems are a great option for growing smaller plants. The drawback with this system is that they can be inefficient if not set up properly, plant growth will be hampered.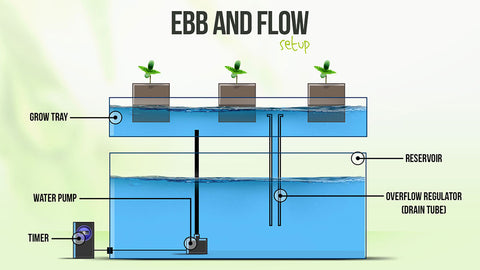 After a period of time, the solution is allowed to drain back into the reservoir. Controlled by a submerged pump with timer, this process of flooding occurs several times a day. While this method is using energy and water efficiently, plant roots can dry out quickly if environmental conditions are off or if the schedule falters due to mechanical failure.
After a period of time, the solution is allowed to drain back into the reservoir. Controlled by a submerged pump with timer, this process of flooding occurs several times a day. While this method is using energy and water efficiently, plant roots can dry out quickly if environmental conditions are off or if the schedule falters due to mechanical failure.